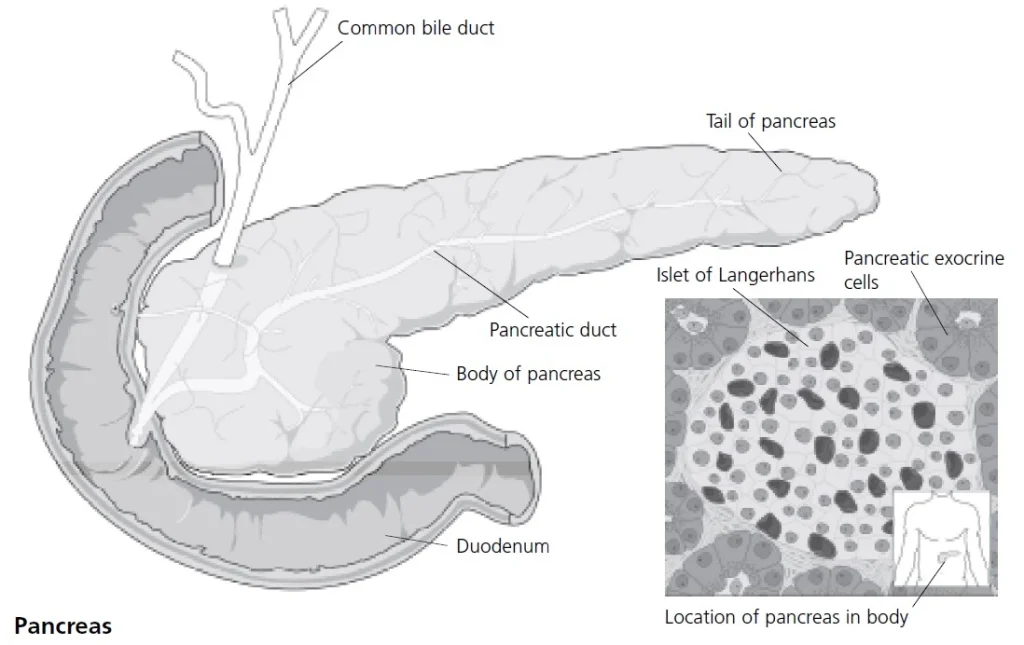
The endocrine tissue found in the pancreas islets form the basis of blood sugar control. Alpha (A) cells in the periphery of the islet tissue secrete glucagon, a polypeptide hormone that increases blood sugar. It binds to glycogen receptors on the liver and induces the enzymatic breakdown of glycogen to glucose. Glucagon also functions in the formation of glucose from the amino acids in the liver through a process called gluconeogenesis.
Adjacent to the alpha cells are the beta cells. They constitute 70% of the islet cells and function to lower blood sugar with the secretion of insulin that is essential for the uptake of glucose from the blood into the majority of the body’s cells.
Virtually all cells use insulin in order to absorb glucose, except for the tissues found in the retina, nerves, and kidney. Insulin is the facilitator that allows sugar to enter the cells by increasing the number of proteins that transport glucose across cell membranes into muscle cells, adipocytes, white blood cells, and certain other cells. Insulin also increases the synthesis of glycogen from glucose in liver cells. However, in the tissues where insulin is not required for the entry of glucose into the cell, the excess glucose that freely enters the cells is broken down into sugar alcohols (polyols). When in excess, these sugar alcohols are the cause of secondary complications of diabetes found in the retina, nerves, and kidneys.
The effects of insulin are numerous, including mediating storage of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and proteins. It is also used in facilitating cellular growth and in enhancing liver, adipose, and muscle metabolism.
Decreased insulin secretion or decreased numbers of insulin receptors are the main causes of impaired
glucose intolerance.
Quick Reference: Major Blood Metabolism Disorders
| Blood Metabolism Disorder | Major Signs and Symptoms | Key Laboratory Tests | Conventional Therapies | Naturopathic Therapies |
| Diabetes Type I | Weight loss | High glucose High glyc, hemoglobin High fructosamine levels | Insulin | Insulin |
| Diabetes Type II | Obesity | High glucose High glyc, hemoglobin High fructosamine levels | Sulfonylurea Biguanides | Botanical medicine, low glycemic diet, chromium, vanadium sulfate, exercise |
| Hyperinsulinemia | Acanthosis nigracans (darkening of the skin) Obesity | High insulin levels, possibly high glucose levels | Biguanides | Botanical medicine, low glycemic diet, chromium, vanadium sulfate, exercise |
| Reactive Hypoglycemia | Irritable when missing meals | none | none | Chromium, vanadium sulfate, botanical medicine |